The pellet machine is a device for compressing biomass pellet fuel and pellet feed, among which the pressure roller is its main component and vulnerable part. Due to its heavy workload and harsh working conditions, even with high quality, wear and tear are inevitable. In the production process, the consumption of pressure rollers is high, so the material and manufacturing process of pressure rollers are particularly important.

Failure analysis of the pressure roller of the particle machine
The production process of the pressure roller includes: cutting, forging, normalizing (annealing), rough machining, quenching and tempering, semi precision machining, surface quenching, and precision machining. A professional team has conducted experimental research on the wear of biomass pellet fuels for production and processing, providing a theoretical basis for the rational selection of roller materials and heat treatment processes. The following are the research conclusions and recommendations:
Dents and scratches appear on the surface of the pressure roller of the granulator. Due to the wear of hard impurities such as sand and iron filings on the pressure roller, it belongs to abnormal wear. The average surface wear is about 3mm, and the wear on both sides is different. The feed side has severe wear, with a wear of 4.2mm. Mainly due to the fact that after feeding, the homogenizer did not have time to evenly distribute the material and entered the extrusion process.
Microscopic wear failure analysis shows that due to the axial wear on the surface of the pressure roller caused by the raw materials, the lack of surface material on the pressure roller is the main cause of failure. The main forms of wear are adhesive wear and abrasive wear, with morphology such as tough pits, plow ridges, plow grooves, etc., indicating that the silicates, sand particles, iron filings, etc. in the raw materials have serious wear on the surface of the pressure roller. Due to the action of water vapor and other factors, mud like patterns appear on the surface of the pressure roller, resulting in stress corrosion cracks on the surface of the pressure roller.
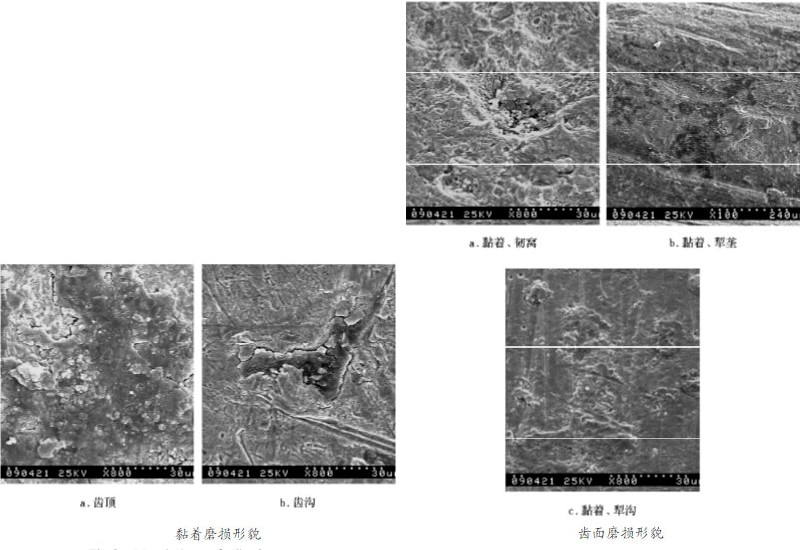
It is recommended to add a impurity removal process before crushing the raw materials to remove sand particles, iron filings, and other impurities mixed in the raw materials, in order to prevent abnormal wear and tear on the pressure rollers. Change the shape or installation position of the scraper to evenly distribute the material in the compression chamber, preventing uneven force on the pressure roller and exacerbating wear on the surface of the pressure roller. Due to the fact that the pressure roller mainly fails due to surface wear, in order to improve its high surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, wear-resistant materials and suitable heat treatment processes should be selected.
Material and process treatment of pressure rollers
The material composition and process of the pressure roller are the prerequisites for determining its wear resistance. The commonly used roller materials include C50, 20CrMnTi, and GCr15. The manufacturing process uses CNC machine tools, and the roller surface can be customized with straight teeth, oblique teeth, drilling types, etc. according to needs. Carburization quenching or high-frequency quenching heat treatment is used to reduce roller deformation. After heat treatment, precision machining is carried out again to ensure the concentricity of the inner and outer circles, which can prolong the service life of the roller.
The importance of heat treatment for pressure rollers
The performance of the pressure roller must meet the requirements of high strength, high hardness (wear resistance), and high toughness, as well as good machinability (including good polishing) and corrosion resistance. Heat treatment of pressure rollers is an important process aimed at unleashing the potential of materials and improving their performance. It has a direct impact on manufacturing accuracy, strength, service life, and manufacturing costs.
For the same material, materials that have undergone overheating treatment have much higher strength, hardness, and durability compared to materials that have not undergone overheating treatment. If not quenched, the service life of the pressure roller will be much shorter.
If you want to distinguish between heat-treated and non heat-treated parts that have undergone precision machining, it is impossible to distinguish them solely by hardness and heat treatment oxidation color. If you do not want to cut and test, you can try to distinguish them by tapping sound. The metallographic structure and internal friction of castings and quenched and tempered workpieces are different, and can be distinguished by gentle tapping.
The hardness of heat treatment is determined by several factors, including material grade, size, workpiece weight, shape and structure, and subsequent processing methods. For example, when using spring wire to make large parts, due to the actual thickness of the workpiece, the manual states that the heat treatment hardness can reach 58-60HRC, which cannot be achieved in combination with actual workpieces. In addition, unreasonable hardness indicators, such as excessively high hardness, can result in the loss of toughness of the workpiece and cause cracking during use.

Heat treatment should not only ensure a qualified hardness value, but also pay attention to its process selection and process control. Overheated quenching and tempering can achieve the required hardness; Similarly, under heating during quenching, adjusting the tempering temperature can also meet the required hardness range.
The Baoke pressure roller is made of high-quality steel C50, ensuring the hardness and wear resistance of the particle machine pressure roller from the source. Combined with exquisite high-temperature quenching heat treatment technology, it greatly extends its service life.
Post time: Jun-17-2024
